Coordinated Public Transit-Human Services Transportation Plan for the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization
Project Manager
Alicia Wilson
Project Principal
Pam Wolfe
GIS
Mary McShane
Paul Reim
Cover Design
Jane Gillis
The preparation of this document was supported
by the Federal Highway Administration through
MassDOT 3C PL contract # 84053 and Federal Transit Administration Section 5303 through MassDOT contract #78923.
Central Transportation Planning Staff
Directed by the Boston Region Metropolitan
Planning Organization. The MPO is composed of
state and regional agencies and authorities, and
local governments.
TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE
2.1 Eligible Projects and Recipients
2.2 MPO projects funded under the new freedom program
TABLE 1 New Freedom Projects in the Boston Region MPO: 2008-2013
TABLE 2 New Freedom Projects by Project Type: 2008–2013
TABLE 3 Boston Region MPO Population with Disabilities by Age Group
Figure 1 Population Age 65 or Older by Municipality
Figure 2 Percentage of Population Age 65 and Older by Municipality
Figure 3 Number of Residents with Disabilities by Municipalities
Figure 4 Percentage of Community Residents with Disabilities
4.1 The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA)
4.2 Cape Ann Transportation Authority
4.3 Greater Attleboro Taunton Regional Transit Authority (GATRA)
4.4 MetroWest Regional Transit Authority
4.5 Montachusett Regional Transit Authority (MART)
4.6 Brockton Area Transit (BAT)
4.7 Boston Region MPO Clean Air and Mobility Program Services
4.8 Massachusetts Port Authority (MassPort) Transit Services
4.10 Transportation Management Association (TMA) Shuttles
4.11 University-Contracted Shuttle (Public Service)
4.12 Private Carrier Routes (stopping within Massachusetts)
4.13 Boston Harbor Cruises Ferry Service
4.14 Councils on Aging and Social Service Organizations
4.15 Private Nonprofits Organizations
4.16 Volunteer Driver Programs
5.2 Regional Coordinating Councils
5.3 Identified Unmet Transportation Needs
6.1 Service Coordination as a Regional Priority
Federal surface transportation funding legislation, the Safe Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act (SAFETEA-LU) was signed into law on August 10, 2005. This legislation established the requirement for a locally developed, Coordinated Public Transit–Human Services Transportation Plan (Coordinated Plan) to obtain funding for projects from Federal Transit Administration human-services transportation programs.
These programs included: 1) Elderly Individuals and Individuals with Disabilities (Section 5310); 2) Job Access and Reverse Commute (JARC, Section 5316); and 3) New Freedom (Section 5317). (The goal of the New Freedom grant program was to reduce barriers to transportation services and expand the transportation mobility options available to people with disabilities beyond the requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990).
The Coordinated Plan was expected to improve transportation services for elderly individuals, people with disabilities, people with low incomes, and to reverse commuters by maximizing collective coverage, minimizing duplication of services, and facilitating the most cost-effective transportation possible with available resources. The Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) completed its Coordinated Plan in 2008 and updated it in 2010.
As a sub-recipient of federal funds, the MPO has supported selection of projects for Sections 5316 and 5317 funding by soliciting projects, evaluating proposals, and recommending projects to the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT)—the direct recipient of funds—for funding. MassDOT has made the final funding decisions for these two programs; and has solicited projects for 5310 funding on a statewide basis and evaluated projects’ consistency with the relevant MPO’s Coordinated Plan.
Congress signed new surface transportation funding legislation, Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century (MAP-21), on July 6, 2012. This was a two-year authorization due to end on September 30, 2014, but provisions and funding have been extended until May 31, 2015. This legislation eliminated JARC as a stand-alone program, eliminated New Freedom as a stand-alone program, and incorporated New Freedom activities into the 5310 program. On June 6, 2014, the Federal Transit Administration (FTA) issued the FTA C 9070.1G Circular, Guidance and Application Instructions: Enhanced Mobility of Seniors and Individuals with Disabilities Program Guidance and Application Instructions. According to the circular introduction, it is a reissue of guidance under 49 U.S.C. 5310 (SAFETEA-LU) that incorporates provisions of MAP-21. A Coordinated Plan is still required for Section 5310 funding.
This updated Coordinated Plan reflects the realities of current legislation. It documents the region’s human service transportation needs and provides ideas for improving transportation services. It also serves as a resource that cites the types of projects initiated, and which projects have been effective.
2 Section 5310: Enhanced Mobility of Seniors and Individuals Under Map-21
This program is intended to enhance mobility for seniors and persons with disabilities by providing funds for programs to serve the special needs of transit-dependent populations beyond traditional public transportation services and Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) complementary paratransit services. Section 5310 funds will pay for as much as 50 percent of operating costs and 80 percent of capital costs. Mobility management and purchase of service are considered capital costs.
The 5310 program was established in 1975 as a discretionary capital assistance program for private non-profit organizations. Under MAP-21, it has evolved to include capital and operating assistance. Traditional Section 5310 projects allow for capital costs associated with buying accessible vehicles, equipment, and transportation services among others. Recipients for “traditional” Section 5310 projects include:
“Other” eligible projects include capital and operating costs and New-Freedom-type projects such as mobility management and travel training. Eligible sub-recipients for “other” Section 5310 projects include:
During the six-year period in which the MPO has evaluated project proposals for New Freedom projects and recommended proposals to MassDOT for funding, 15 entities in the MPO received approximately $5.75 million for 22 projects (ongoing projects funded in different solicitations for additional years’ funding for the same project are counted as one project). Table 1 lists the number of projects by type of service and primary service goals.
TABLE 1
New Freedom Projects in the Boston Region MPO: 2008-2013
Project |
Expanded Geographic Coverage |
Extended Hours/ Days of Service |
Improved System Capacity |
Improved Access/ Connections |
Improved Customer Knowledge |
Planning for Services |
Total |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Trip Based |
6 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
10 |
45% |
Information Based |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
8 |
36 |
Capital Investments |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
18 |
Total |
7 |
1 |
1 |
6 |
6 |
1 |
22 |
100% |
Pct. of Total |
32% |
5% |
5% |
27% |
27% |
5% |
100% |
Source: CTPS.
The majority of funded projects are either trip based (45%) or information based (36%). Less than 20% (18%) are capital investments (purchasing vehicles and equipment). Approximately one-third (32%) of the projects were intended to expand geographic coverage; another 27% were intended to improve customer knowledge. Approximately one-quarter (27%) of the projects had the goal of improving access and connections.
Table 2 presents sub-categories of project types. The sub-categories were taken from a national evaluation of JARC and New Freedom projects. Not all New Freedom projects in the MPO fit neatly into specific project types. Some projects are a combination of types but are listed under one project type.
TABLE 2
New Freedom Projects by Project Type: 2008–2013
Project Type |
Number of Projects |
Pct. Total Projects |
|---|---|---|
Trip-Based Services |
10 |
45% |
Shuttle/Feeder Service |
2 |
9% |
Expanded Paratransit Service |
1 |
5% |
Same-Day Paratransit Service |
1 |
5% |
Door-to-Door Service |
4 |
18% |
User-Side Vouchers |
2 |
9% |
Information-Based Services |
8 |
36% |
Mobility Manager |
1 |
5% |
Travel Training |
1 |
5% |
Internet Based Information |
2 |
9% |
Mobility Management (combination of services) 1 |
4 |
18% |
Capital Investment |
4 |
18% |
Vehicles |
3 |
14% |
ITS-related Hardware/Software Improvements |
1 |
5% |
Total |
22 |
100.0% |
1Includes Travel Training, One-Call Centers, and trip planning.
ITS = Information Technology Services.
Source: CTPS.
Varied projects were funded under the New Freedom program. Several have had long-lasting effects and have become models for other agencies and programs. Among these projects are:
A list of funded New Freedom projects in the MPO is included in Appendix A.
The MPO’s original Coordinated Plan and update used 2000 US Census data. New Census data has become available. The following information uses the 2010 US Census and 2006–2010 and 2008–2012 American Community Survey (ACS) data.
There are various thresholds for who is considered a senior depending on program types and activities. The American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) offers cards to those who are 50 years of age. Some restaurant senior discounts start at 55. Some retail stores offer discounts to those who are at least 60 years of age. MBTA senior identification cards are available to those who are at least 65 years old. Various pieces of federal legislation apply the senior determination to the age at which pensions, social security or medical benefits for seniors become available. Traditionally, people in the United States have been eligible to retire with full Social Security benefits at age 65. (The age threshold for full benefits has increased slightly for those born after 1942.) Medicare also begins at age 65. The Section 5310 Circular defines a senior as an individual who is 65 years of age or older.
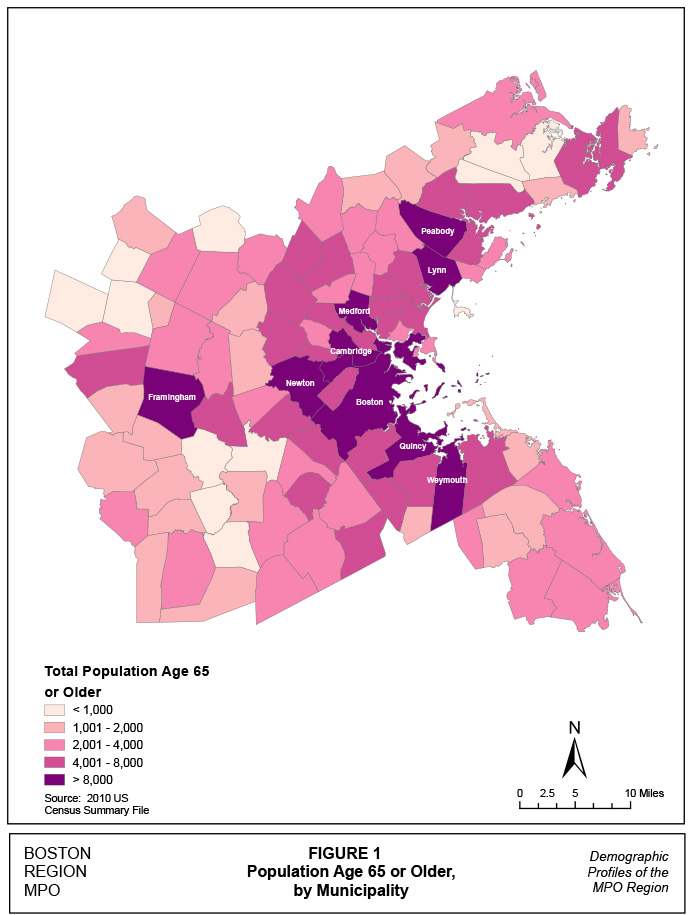
Older adults are not confined to particular communities in the MPO. They are located throughout the region. The 2010 US Census indicates that 13.4% of the region’s population is 65 years of age or older. Representation in the population ranges from a low of 7.9% in Hopkinton to a high of 23% in Rockport. Four communities’, Rockport, Concord, Nahant, and Peabody, senior population is more than 20% of the total population. Figures 1 and 2 show numbers and percentages, respectively, of seniors by MPO community.
Metropolitan Area Planning Council (MAPC) status quo population projections indicate that by 2030, the senior population will account for 16% of the total population and will have increased by 28% since 2010.
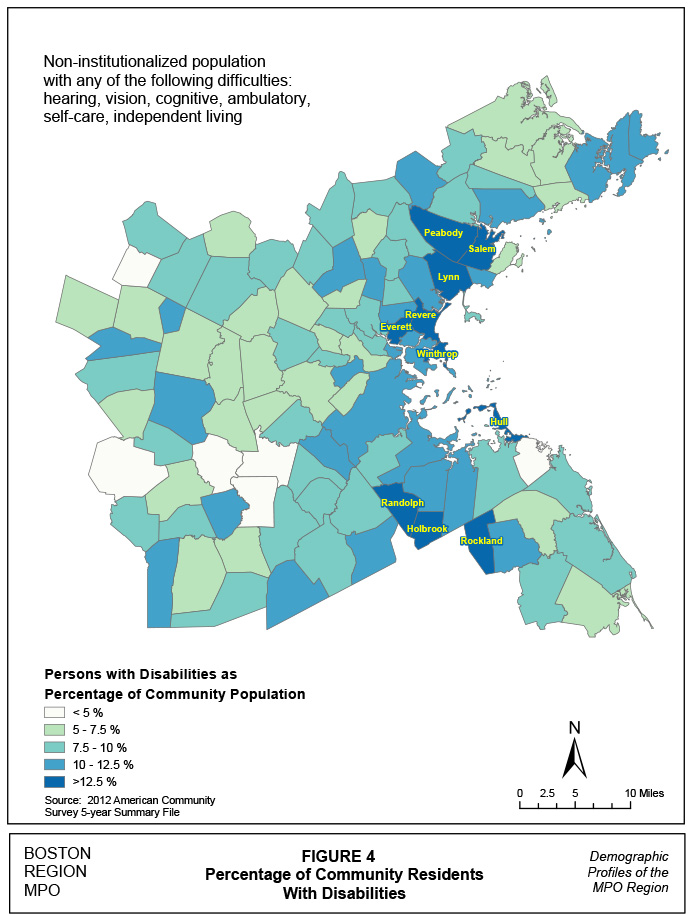
According to the ACS, the un-institutionalized civilian population with disabilities represents approximately 10% of the region’s population. As with seniors, persons with disabilities are not isolated in any particular part of the region (see Figures 3 and 4). However, clusters representing more than 12.5% of the population occur in 10 communities to the North and South. The Northern communities include: Everett, Lynn, Peabody, Revere, Salem, and Winthrop. Communities to the south include: Holbrook, Randolph, and Rockland. Municipal percentages range from a low of 2.5% in Sherborn to a high of 14.6% in Revere.
Table 3 indicates that the percentage of population with disabilities by age group does not correspond with the representation of that age group in the general population. For example, 18-34 year olds account for 26% of the general population, but only 11% of the population with disabilities. Persons who are 75 years old or older represent 6% of the general population and 30% of the population with disabilities. Forty-four percent of the population with disabilities is age 65 or older.
TABLE 3
Boston Region MPO Population1 with Disabilities by Age Group
Age |
Total Population |
Population with Disabilities |
Percent Population |
Percent Population with Disabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Younger than 5 Yrs. |
177,066 |
1,127 |
5.6% |
0.4% |
5-17 Years |
479,067 |
23,130 |
15.3 |
7.5 |
18-34 Years |
805,430 |
32,819 |
25.7 |
10.6 |
35-64 Years |
1,266,109 |
116,556 |
40.4 |
37.6 |
65-74 Years |
211,671 |
44,511 |
6.8 |
14.4 |
75+ Years |
196,459 |
91,778 |
6.3 |
29.6 |
Total |
3,135,802 |
309,921 |
100.0% |
100.0% |
1Un-institutionalized population.
Source: 2008-2012 American Community Survey Summary File.
Analysis shows that approximately half (51%) of the population with disabilities who live in households meet the MPO’s low-income threshold. Less than half (44%) of seniors in households meet the low-income threshold.
Figure 1
Population Age 65 or Older by Municipality

Figure 2
Percentage of Population Age 65 and Older by Municipality
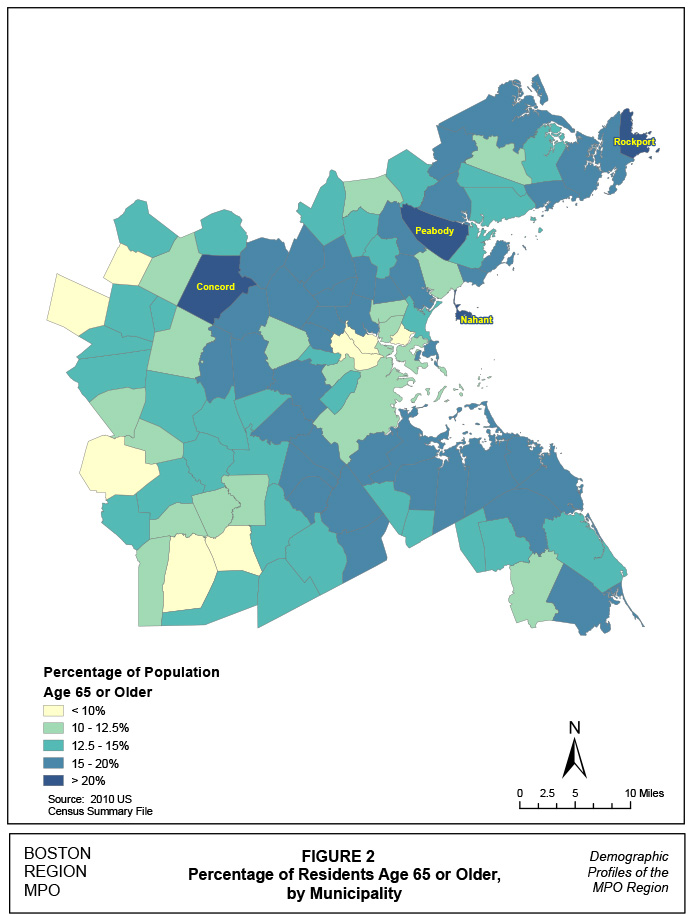
Figure 3
Number of Residents with Disabilities by Municipalities
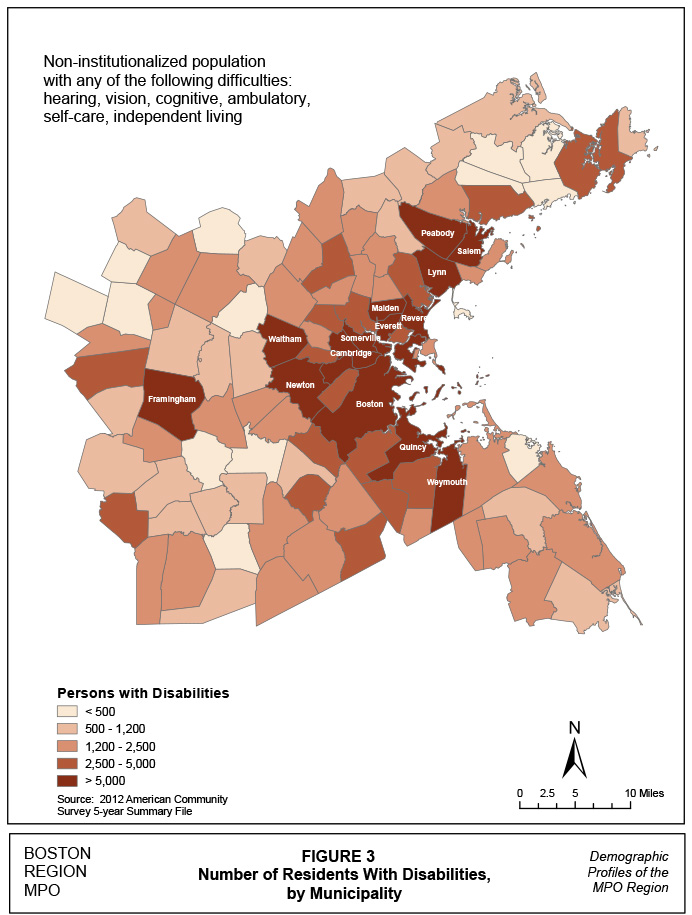
Figure 4
Percentage of Community Residents with Disabilities
The Boston Region MPO area is served by a number of different transportation service providers, including the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA); several smaller regional transit authorities (RTAs); local transportation management associations; municipal, and nonprofit providers that offer a broad range of services. Several municipalities in the Boston Region MPO area have no direct affiliation with regional transit authorities (RTAs) and have no local MBTA or RTA bus or van service. These communities include: Hamilton, Hanover, Manchester, Milford, Millis, North Reading, and Norwell.
The MPO developed, for the 101 municipalities in the region, a database with services provided to seniors and people with disabilities. The database was updated during the summer of 2014 and will be posted on the MPO website. The original database has been posted at www.bostonmpo.org/geoserver/www/apps/tseApp/index.html.
Information in this section was compiled from multiple sources, including MBTA and Boston Region MPO documents and various websites (such as RTAs, transportation management areas, and social service agencies).
The MBTA is the primary transit provider in the Boston region. It directly operates or hires contractors to operate heavy rail, light rail, bus rapid transit, local/express bus, trackless trolley, commuter rail, commuter boat, and paratransit service. The MBTA fixed-route system is predominantly a hub-and-spoke network that serves 175 municipalities. The MBTA’s commuter rail service extends beyond the Boston Region MPO area. MBTA local bus service extends from Boston to just beyond Route 128; heavy rail, light rail, and bus rapid transit service is mostly limited to municipalities within Route 128. Commuter boat services link two locations in Boston and extend to two municipalities on the South Shore.
The MBTA system serves 140 stations located on six transit lines: Red Line, Mattapan High Speed Line, Orange Line, Blue Line, Green Line, and Silver Line.
The MBTA operates more than 170 bus routes and four electric trackless trolley routes serving 44 municipalities. All but 10 of these routes serve a rapid transit (light or heavy rail) station, but those 10 routes provide service to commuter rail stations. In areas close to the urban core, buses provide crosstown service and feeder service to rapid transit stations. Buses operating outside the urban core provide local service, feeder service to rapid transit and some commuter rail branches, and express service to Boston.
The MBTA commuter rail network is composed of 12 radial lines, with 138 stations (103 of which are accessible), and 394 miles of track. It directly serves 81 municipalities in both Massachusetts and Rhode Island. Another station, Wachusett, is under construction on the Fitchburg line and is scheduled to open in 2015. Commuter rail service is provided at two downtown Boston terminals, North Station and South Station. The Massachusetts Turnpike is generally considered a dividing line between the northern and southern commuter rail routes. All routes operating north of the Turnpike (Rockport/Newburyport, Haverhill, Lowell, and Fitchburg lines) operate to and from North Station; and all routes operating along the Turnpike or to the south of the Turnpike (Framingham/Worcester, Needham, Franklin, Providence/Stoughton, Fairmount, Middleborough/Lakeville, Kingston/Plymouth, and Greenbush lines) operate to and from South Station. Commuter rail service provides weekly inbound and outbound trips, with headways ranging from 25 to 40 minutes during the peak periods, to up to four hours during off-peak periods.
The MBTA contracts with private carriers to provide THE RIDE service, a paratransit service for people who are not able to fully utilize fixed-route public transportation because of disabilities. THE RIDE is a shared-ride, advance-request service that operates sedans and lift-equipped vans in 60 municipalities, 365 days a year, generally from 5:00 AM to 1:00 AM. THE RIDE is administered by the MBTA’s Office for Transportation Access (OTA), in compliance with the ADA, in the following communities (an asterisk denotes partial coverage): Abington*, Arlington, Avon*, Bedford, Belmont, Beverly, Billerica*, Boston, Braintree, Brockton*, Brookline, Burlington, Cambridge, Canton, Chelsea, Cohasset, Concord, Danvers, Dedham, Dover, Everett, Hingham, Holbrook, Hull, Lexington, Lincoln, Lynn, Lynnfield, Malden, Marblehead, Medfield, Medford, Melrose, Middleton, Milton, Nahant, Needham, Newton, Norwood, Peabody, Quincy, Randolph, Reading, Revere, Salem, Sharon, Saugus, Somerville, Stoneham, Stoughton*,Swampscott, Topsfield, Wakefield, Walpole, Waltham, Watertown, Wellesley, Wenham, Weston, Westwood, Weymouth, Wilmington, Winchester, Winthrop, and Woburn.
Local wheelchair-accessible fixed-route minibus services are provided in Beverly, Bedford, Burlington, Dedham, Lexington, and the Mission Hill neighborhood of Boston with subsidies from the MBTA’s Suburban Transportation Program. All of these services connect with MBTA services; the services provided in Bedford and Lexington connect with each other and with Lowell Regional Transit.
In 2012, the most recent information available, the MBTA operated 98,053,683 annual vehicle revenue miles with 2,352 vehicles in maximum service.
The Cape Ann Transportation Authority (CATA) is a public agency that serves the city of Gloucester and the towns of Rockport, Essex, and Ipswich. CATA provides fixed-route and a door-to-door Dial-A-Ride service via a contract with the Cape Ann Transportation Operating Company. Dial-a-Ride service is available in Gloucester, Rockport, Essex, and Ipswich, and as organized trips outside of the Cape Ann region Monday through Friday from 9:00 AM to 2:30 PM. Persons older than 60 years of age and adults with disabilities are eligible to use the service. CATA’s fixed-route service includes six routes that operate in and between Gloucester and Rockport, Monday through Friday from 6:00 AM to 7:00 PM, and Saturday from 9:00 AM to 6:00 PM. CATA also offers advance-request paratransit service in Gloucester and Rockport only for those who are unable to use fixed-route transportation. The service runs during fixed-route hours. In 2012, CATA operated 481,559 annual vehicle-revenue-miles, with 22 vehicles operating in maximum service. CATA service operates entirely within the Boston Region MPO area.
GATRA provides public transportation services to 28 member communities; the 11 communities in the Boston Region MPO area are: Bellingham, Duxbury, Foxborough, Franklin, Hanover, Marshfield, Medway, Norfolk, Pembroke,Scituate, and Wrentham. GATRA also leases vehicles to two councils on aging and leases 16 intercity coaches to three private operators. GATRA services include fixed-route bus service, paratransit service for elderly individuals and people with disabilities, and Medicaid and human-services transportation services. In Franklin, Foxborough, Norfolk, and Wrentham, GATRA also provides Dial-a-Ride and long-distance medical transportation for seniors and people with disabilities to Boston and other destinations (such as Burlington, Framingham, Newton, and Worcester) via the Miles for Health program, as well as service to Boston Hospitals and the greater South Shore Hospital area via the Boston Hospital Bus. In 2012, GATRA operated 3,197,594 annual vehicle-revenue-miles with 112 vehicles operating in maximum service. GATRA also provides bus service to several MBTA stations, including commuter rail stations in Franklin and Norfolk, which are located within the Boston Region MPO area.
GATRA started providing wheelchair-accessible fixed-route service and ADA-compliant van service in Franklin on March 10, 2008 with a grant from the Boston Region MPO’s Suburban Mobility Program (later known as the Clean Air and Mobility Program). Transit service GATRA operates in Franklin and Bellingham began with a JARC grant (2008) to provide additional transit service to low-income workers. The commuter rail shuttle in Pembroke was started in 2009 with JARC and New Freedom grants to operate demand-responsive service in Pembroke and a commuter rail shuttle service.
The MetroWest Regional Transit Authority (MWRTA) was formed in 2006. MWRTA currently provides fixed-route bus service on twelve routes (from 6:00 AM until 9:00 PM) in and between the municipalities of Ashland, Dover, Framingham, Holliston, Hopkinton, Hudson, Marlborough, Natick, Sherborn, Southborough, Sudbury, Wayland, Wellesley, and Weston. MWRTA also provides ADA-compliant transit service to these areas and operates paratransit service in Framingham and Natick that is equivalent to THE RIDE service.
The Green Line shuttle (Route 1) began operating in March 2009. The Suburban Mobility Program funded the first year of service with capital support for purchasing vehicles through a JARC grant awarded in 2008. This service also received JARC grants in subsequent years.
Service in Wellesley, (Route 8) began operating in 2013. It provides service between many residential and commercial destinations in Wellesley between the Natick Mall and the Woodland Green Line Station. Route 8 provides commuter service between 6:20–8:30 AM and 5:11–7:30 PM, with a local circular route in between. A JARC grant for this service was awarded in 2013.
Route 7 serves Framingham, Southborough and Marlborough, with service coverage along Route 9, and Route 85. Major stops include Marlborough City Hall, Staples Drive, Framingham State University and Downtown Framingham. Saturday service is also available. A JARC grant for this service was awarded in 2010.
In 2012, MWRTA operated 1,548,692 vehicle-revenue-miles with 57 vehicles operating at times of maximum service.
MART provides council-on-aging transportation service for Bolton, Boxborough, and Littleton residents who are elderly or have disabilities. It also provides transportation brokerage services for the Department of Public Health Early Intervention Program, Department of Developmental Services, Special Education Transportation Services, and MassHealth within the Boston metropolitan region.
BAT provides fixed-route bus service between Brockton and the MBTA’s Ashmont Station, with stops in Randolph and Milton.
In federal fiscal year 2002, the MPO implemented its Suburban Mobility Program to provide funding for public transit services in suburban areas that are underserved by existing transit service. This program later evolved to become the Clean Air and Mobility Program. These programs have allocated Congestion Mitigation Air Quality (CMAQ) funding for starting up new, locally developed and supported transit services that improve air quality and reduce congestion. CMAQ funding, through the Boston Region MPO, is limited to three years, after which a project must be self-sustaining.
Services originally funded through this program and now operating on their own include:
The MPO continues to support the Clean Air and Mobility Program in its Long-Range Transportation Plan, but, because of funding constraints in the Transportation Improvement Program (TIP), has not conducted a solicitation or programmed funds since FFY 2012.
MassRIDES, a MassDOT service, provides free statewide travel-options assistance to employers and other travelers. The program includes an active employer-based partnership program; statewide ridematching; vanpool formation and support program; extensive coordination with 16 regional transit authorities; a statewide, toll-free bilingual customer-service telephone line; and the Massachusetts Safe Routes to School program. MassRIDES promotes carpooling and vanpooling through a statewide ridematching database of more than 15,400 commuters who register for MassRIDES programs and services.
These transit services, funded by TMAs, provide transportation for employees of the TMA membership and sometimes for members of the general public.
University of Massachusetts, Boston (UMass Boston) offers frequent shuttle service to JFK/UMass Station (MBTA Red Line) and JFK Library and Museum.
Boston Harbor Cruises operates seasonal (May-October) ferry service between Salem and Long Wharf in Boston and Lynn and Central Wharf in Boston. The company also operates year-round water taxi service between Logan Airport and the Boston Waterfront with many stops along the way.
Most municipalities in the MPO region have councils on aging that own and operate shuttle service for elderly residents who live in the municipality that provides the service. In addition, there are several nonprofit social service organizations that operate transit service for their clients. The MPO has documented services available in each community. This data is located at www.bostonmpo.org/geoserver/www/apps/tseApp/index.html.
Goals of Coordinated Plan
The goals of this Coordinated Plan are to 1) inventory transportation resources; 2) document transportation needs of seniors and those with disabilities; and 3) improve transportation services for these groups—by identifying opportunities to pool resources to maximize the amount of service provided with those resources.
Background
Demographic analysis shows that populations of elderly individuals and people with disabilities are dispersed throughout the MPO region. People in these groups are often less able than the rest of the population to use traditional transit services. The need for special services increases as more and more seniors are aging in place and their ability to drive, individual mobility, or other capability declines with age. The general public and supporting agencies helped to identify and prioritize the needs of elderly individuals and people with disabilities reported in this update of the Coordinated Plan. An added, and important, component of this update is information collected from three special forums and the ongoing work of the statewide Mobility Management Program’s Regional Coordinating Councils. Section 5.3 below discusses transportation needs that were identified through coordination and consultation.
In 2011, the governor of Massachusetts signed Executive Order 530 establishing a commission to reform community, social service, and paratransit transportation services to coordinate transportation resources more efficiently and effectively. The Commission published a final report, Community, Social Service, and Paratransit Transportation Commission Report, in 2012, with recommendations addressing the areas of coordination and efficiency.
The RCCs
Two of the report’s major recommendations were to create an advisory council at the state level, otherwise known as Statewide Coordinating Council on Community Transportation (SCCCT), and to form Regional Coordinating Councils (RCCs) to address community transportation and paratransit service gaps at the local level. The Massachusetts Department of Transportation’s (MassDOT) Rail and Transit Division has a mobility manager who is responsible for statewide mobility management. The mobility manager facilitates the work of the SCCCT and RCC formation and activity. RCCs are voluntary advisory bodies that provide the opportunity for a variety of local stakeholders to3:
- Identify unmet transportation needs, articulate regional priorities, and build coalitions around new projects in mobility and transportation
- Coordinate existing services at the local level to serve more people and increase sustainability of services
- Communicate local unmet needs and mobility priorities to planning agencies (for their coordinated plan updates), MassDOT, the Executive Office of Health and Human Services (EOHHS), and other state agencies
- Participate in a statewide campaign to raise awareness of the important role that community transportation services play for seniors, people with disabilities, and all Massachusetts residents
Ten RCCs have been established to date. Five of these RCCs have coverage areas that include approximately half of all MPO communities. (Two additional RCCs in the MPO region are in initial formation stages.) Each RCC surveys constituents, identifies needs and gaps in transportation services, and develops priorities. RCCs are not all the same as they serve different areas and constituencies and are in different stages of development. However, they all have the same overarching task of improving transportation and transportation options for the elderly and persons with disabilities.
The general public, agencies, and private, non-profit organizations have had the opportunity to provide information for this updated plan through forums, meetings, surveys, and RCC activities throughout 2013 and 2014. The following section describes the various activities and information obtained from them.
5.1 MPO Public Input
Human Services and Equity in Transportation Forum
The Boston Region MPO, in conjunction with MAPCEOHHS, and MassDOT’s Rail and Transit Division’s mobility manager, held a forum on Human Services and Equity in Transportation on January 14, 2014. The purpose of the forum was to bring together agencies and organizations working in the field of human services and community transportation to share information and experiences. More than 60 people, representing many agencies and organizations, attended.
The forum included a panel discussion and a breakout session, during which groups were asked to discuss the following topics and questions:
- Transportation services in their areas:
- Gaps—if any—in their service areas
- Additional services they would like to see in their service areas
- If they were familiar with any successful programs in or outside of their service areas that they thought might work well in their neighborhoods
- Where they see opportunities for coordination among services and for collaboration among providers
- What, if anything, prevents coordination and collaboration from taking place in their areas?
Access Advisory Committee to the Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority forum (AACT), November 2013
This forum brought together the MBTA general manager and members of her staff, AACT members, and representatives from paratransit service providers to discuss accessibility issues.
Regional Transportation Advisory Council Community Transportation Forum: Meeting Local Needs Through Cooperation and Coordination, September 2014
This forum’s panel discussion included the following topics (members of the general public were invited):
- Sustainability for ADA paratransit within the Greater Boston region
- An overview of the statewide mobility management program and work of the RCCs
- A review of statewide transportation programs and services available for seniors and opportunities for sharing resources
- A review of a TMA’s transportation network, program development, and engagement with private partners
- A discussion of the CrossTown Connect inter-municipal transit service, which demonstrates innovative local transportation programs and coordinated services
Transportation Equity Survey
A survey soliciting the transportation concerns of minority and low-income communities, elders, persons with disabilities, and persons with limited English proficiency was distributed through the MPO’s Transportation Equity email list and is posted on the MPO’s website. A version of this survey also was handed out at forums.
5.2 Regional Coordinating Councils
Ten RCCs currently are active around the state; five of them encompass more than half of the communities in the MPO. These RCCs are in various stages of assessing and prioritizing needs. RCCs within the MPO and the methods they used to assess needs are described below. Unless otherwise noted, member communities are located entirely within the MPO.
Brockton Area RCC
Coverage Area (MPO communities in italics):
Abington, Avon, E. Bridgewater, W. Bridgewater, Bridgewater, Brockton, Easton, Halifax, Rockland, Stoughton, Weymouth and Whitman
Methods used to assess unmet needs:
Surveyed stakeholders
Greater North Shore RCC
Coverage Area:
Beverly, Danvers, Essex, Everett, Gloucester, Hamilton, Ipswich, Lynn, Lynnfield, Malden, Manchester, Marblehead, Medford, Melrose, Middleton, Nahant, North Reading, Peabody, Reading, Rockport, Rowley, Salem, Saugus, Stoneham, Swampscott, Topsfield, Wakefield, and Wenham
Methods used to assess unmet needs:
- Proceedings from breakout sessions that identified elements of livable communities-North Shore Transportation Conference, August 2013
- Unmet needs collected by individual RCC member organizations over time and discussed at the RCC formation meeting in March 2014
Twenty-one mutually exclusive unmet needs emerged, which RCC member organizations ranked via priority voting at the first RCC meeting.4
MetroWest RCC
Coverage Area (non-MPO communities in italics):
Ashland, Dover, Framingham, Holliston, Hopkinton, Hudson, Marlborough, Milford, Natick, Needham, Newton, Sherborn, Southborough, Sudbury, Wayland, Wellesley, Weston, and Westborough
Methods used to assess unmet needs:
This RCC is conducting an unmet transportation needs assessment survey.
Minuteman RCC
Coverage Area (MPO communities in italics):
Acton, Ayer, Bedford, Bolton, Boxborough, Carlisle, Concord, Harvard, Hudson, Littleton, Lexington, Lincoln, Maynard, Shirley, Stow Sudbury, and Westford
Methods used to assess unmet needs:
This RCC is in the process of collecting existing needs studies and contacting member communities concerning their needs.
Southeast RCC
Coverage Area (MPO communities in italics):
Attleboro, Bellingham, Berkley, Carver, Dighton, Duxbury, Foxborough, Franklin, Hanover, Kingston, Lakeville, Mansfield, Marshfield, Medway, Middleborough, Norfolk, North Attleboro, Norton, Pembroke, Plainville, Plymouth, Raynham, Rehoboth, Scituate, Seekonk, Taunton, Wareham, and Wrentham
Methods used to assess unmet needs:
- Unmet transportation needs assessment survey distributed to 169 stakeholders in February 2014
- “Moving Forward Together” regional stakeholder meeting, March 2014
- Unmet trip analysis from RideMatch, a regional transit authority trip planner
- Survey for medical transportation needs assessment fall 2014
5.3 Identified Unmet Transportation Needs
The MPO’s original coordinated plan contained information about service and coordination needs perceived by individuals, organizations, and agencies. While some of these issues have begun to be addressed, the majority are still valid. Needs and service gaps from the previous plan, unmet needs information obtained from recent public input, and needs information from RCCs were divided into the following four categories.
Service and Infrastructure Improvements
- In general, the locations of bus shelters should be improved. More near-side stops and shelters would be beneficial to elderly individuals and individuals with disabilities. (Near-side bus stops are located immediately before an intersection and allow passengers to unload and load while the vehicle is stopped at a red light. They also allow passengers to board the bus immediately adjacent to the crosswalk, minimizing walk distances.)
- The size and capability of the vehicle required for paratransit service should be considered. Many vehicles operate below capacity, and wheelchair-accessible vans are sometimes used when sedans would be more appropriate.
- There is limited access to employment corridors for many because of limited affordable transportation options.
- There are few or no benches at MBTA stations.
- Bus stops need shelters, benches, maps, and schedules.
- Providing access to transit from new developments is important.
- Many transit trips require too many transfers.
- Affordable and accessible community shuttles are needed.
- Even though fares for THE RIDE have decreased, the cost still can deter people from using the service.
- Clearing of curb-cuts, bus stops, handicapped parking spaces, and access ramps during winter months is a must for seniors.
- MBTA elevators are sometimes difficult to find and are frequently out-of-order.
Customer Relations
- All of the transportation providers need to improve customer relations, especially those who interact with elderly people and people with disabilities. Driver training should be uniform and should focus on helping clients feel safe and comfortable.
- The providers’ communication systems need to be improved. Telephone access is often delayed, and Internet or voice-recognition-based reservations would be beneficial. At the very least, individuals should be informed about the best times to call to minimize waiting times.
- Calls to service providers should be free, especially if callers will be put on hold or have to call back frequently to reach a representative.
- Service providers should provide information about their routes and capabilities (for example, door-to-door service, passenger assistance, online reservations, and wheelchair accessibility), as well as how to access services.
- Providers should run public-service announcements on the radio, television, or Internet during the day to market their services.
- Dispatchers sometimes experience language problems when scheduling rides for people for whom English is not their first language.
Coordination
- Universal training and accessibility levels across the state should offer seamless transitions that would provide elderly individuals and people with disabilities the level of comfort needed to allow them to use any service. Current disparities in the level and quality of service cause some individuals discomfort and to have concerns about safety.
- Service across geographic boundaries should be more seamless for people with disabilities; for example, one application, one fare policy, and one customer account across service areas.
- Health care providers often do not ask if and how patients can get to appointments or tests when they are being scheduled.
- Hospitals should be engaged to assist with providing rides for patients when other options are not available.
- Eligibility requirements for THE RIDE and other disability-based services should be expanded to include elderly individuals who cannot drive or who have impairments that limit their driving capabilities.
- Coordination of providers for joint purchases (of things like vehicles and gasoline) could lead to cost savings.
- A system that allows for coordinated dispatch of services would improve efficiency. Many individuals need to use different services for different trip purposes, and it would be more efficient for them to call one center to help them organize their trips.
- The many sources of transportation funding from all agencies should be considered and coordinated when providing transportation services. The budgets for all services should be incorporated into human service transportation planning and policy.
- Intermodal connections need to be improved and better integrated with senior housing, low-income housing, and businesses.
- A catalog of services available by category (for example, wheelchair accessible and service area) in all formats would be a useful and valuable resource.
- Service efficiency could be improved by changing eligibility requirements (for example a council on aging could transport people with disabilities, as well as elderly individuals, to medical appointments) and by eliminating underutilized duplicative services.
- The coordination and branding of services (visual and auditory) would promote better understanding of the many services available in the region.
- Service providers should coordinate to minimize duplication of services and improve intermodal connections.
- Coordination and collaboration among cities, towns and other types of transportation providers is inconsistent and needs to be improved; coordination and collaboration should be initiated where it does not yet exist.
- There is a need to think more broadly, without arbitrary service area boundaries
- Scheduling needs to be more efficient.
- Engage community colleges to better serve low-income students and students with disabilities.
Service Expansion
- Not enough night and weekend service
- Not enough late night and early morning transit
- Service gaps exist within and between communities
- Some geographic areas have limited/ no service
- Not enough service to local medical facilities in general and long-distance medical facilities in particular
- Length of headways on some routes or at some times of day prevents some people from using a service
- Expand geographic coverage and service hours of THE RIDE
- Services provided by councils on aging that are confined by political boundaries restrict mobility
- Many councils on aging limit service to the elderly; could also accommodate people with disabilities
5.4 Unidentified Needs
This plan is not intended to be all inclusive. Needs will continue to be identified and included in future updates.
6 Strategies for Addressing Transportation Needs and Prioritizing Projects
The following strategies can be used to address transportation needs of elderly individuals and people with disabilities and to improve coordination of services.
The examples cited below are not intended to limit the approach taken to meet the goals of the funding program:
- Purchase appropriately sized accessible vehicles
- Purchase radios and communication equipment
- Install vehicle shelters
- Purchase wheelchair lifts and restraints
- Rehabilitate, manufacture, or overhaul vehicles
- Undertake preventive maintenance
- Implement vehicle procurement, testing, inspection, and acceptance costs
- Lease equipment when more cost-effective than purchasing
- Acquire transportation services under a contract, lease, or other arrangement
- Introduce new technology into public transportation
- Increase hours of operation
- Extend hours to meet nontraditional work schedules
- Increase service frequency
- Increase weekend service
- Increase service coverage
- New or expanded routes
- Paratransit services beyond the ADA requirements
- Expand service boundaries
- Improve accessibility of existing services
- Use appropriate vehicles.
- Improve amenities (shelters, maps, signs, non-English signs)
- Improve access to stations/stops
- Offer same-day paratransit service
- Enhance level of service
- Improve and standardize driver training
- Improve communications
- Improve scheduling systems
- Improve service promotion and marketing
- Increase use of information technology to coordinate travel
- Provide travel training and trip planning/counseling resources
- Provide one-on-one travel counseling
- Develop volunteer driver programs
- Catalog available services by type and eligibility
- “Brand” services across providers and educate users about the system
- Create or expand voucher program
- Reduce duplication of services through coordination
- Coordinate services to share vehicles for various programs and needs at different time
- Modify eligibility requirements to allow passengers traveling to the same destinations to ride in the same vehicle
- Allow a person with travel needs under various programs to schedule trips through one center
- Improve intermodal connections
- Engage in mobility management
- Coordinate transportation services
- Develop and operate call centers for dispatch and travel coordination
- Arrange for group purchasing
6.1 Service Coordination as a Regional Priority
Coordination of services and programs is a major theme common to public input and is a key component of Executive Order 530. Coordination can enhance access, minimize duplication of services, and produce cost‐effective solutions. Coordination should be a regional priority.
6.2 Obstacles to Coordination
Even though there is a desire to coordinate, many obstacles are incurred, which include:
- Transportation services for seniors do not always serve those with disabilities well.
- Some vehicles can be used only for specific purposes even though they sometimes operate with no passengers on board.
- There is a possible liability issue when organizing volunteers to perform certain tasks.
- Organizations, councils on aging, and municipalities are financially constrained, and finding funding to implement transportation programs is a problem.
- Parochial attitudes toward vehicle sharing limit cooperation.
- Costs for drivers and equipment maintenance of can be factors that limit the level of service provided and result in some vehicles being underutilized.
The MPO will continue to promote activities, solicit input, and bring various groups, agencies, and individuals together to further discussions and actions involving transportation services and programs for seniors and persons with disabilities.
Appendix. New Freedom Projects in the Boston Region MPO, 2008-2013
Organization
Project Name and Purpose
Project Type
Acton
Taxi Voucher Program
Provide taxi vouchers to the elderly and persons with disabilitiesBecame a mobility Management Program
Acton
CrossTown Connect Dispatch
Increase efficiency by consolidating/ expanding dispatch services for all accessible vans operated by each community in service areaOperating
Cape Ann Transportation Operating Company
Medical HealthLink Shuttle
Provide transportation services from CATA service area to Beverly Hospital, North Shore Regional Dialysis Center, Massachusetts General Hospital/ North ShoreShuttle
Friendship Home
Wheels to Work
Provide transportation to enhance opportunities for people with developmental disabilities to participate in job training, internships, paid employmentOperating
Greater Attleboro Taunton Regional Transit Authority
Pembroke Shuttle
Expand weekday demand-response service hours/ institute limited Saturday service for the elderly and people with disabilities in PembrokeShuttle
Greater Attleboro-Taunton Regional Transit Authority
Enhanced Demand Response
Provide service to medical facilities and other locations in Foxborough area (priority to riders with disabilities and the elderly)Paratransit
Greater Lynn Senior Services
Reaching Beyond Borders
Develop regional mobility management capability to assist elders and adults with disabilities who are not able to access para-transit services, or for whom para-transit services are not available
Project components include a travel counseling call center, volunteer driver program, and kiosks at community locations where consumers work with travel coaches to plan trips, assess critical driving skills, and develop individualized training
Mobility Management and Operating
Greater Lynn Senior Services
Community Planning
Community-wide planning project to create a strategic plan to address mobility barriers across the regionPlanning Mobility Management
Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority
Taxi Voucher Program
Proposes to improve mobility for paratransit customers by subsidizing non-ADA mandated trips via taxi
Trips could include same-day reservations, destinations from or to the new Premium Service area, or to connect to other RTAs; service would be available 24 hours/ day, 7 days/ weekPlanning and Operating
Massachusetts Department of Developmental Services
Mass Advocates Standing Strong
Travel train individuals with intellectual disabilities to participate in policy-formulation activities and other forms of civic engagementTravel Training
Massachusetts Human Services Transportation Office
Evaluation and Planning Study of the Brokerage System
In-depth evaluation and planning study of Massachusetts’ Human Services Transportation regional brokerage system; ways to integrate additional coordination/ mobility management strategies to address barriers and unmet transportation needs for people with disabilities and/or low income, and eldersPlanning Study
Massachusetts Human Services Transportation Office
Mobility Management Information Network Pilot
Build/ maintain online information hub for mobility management and community transportation coordination; conduct community transportation outreach and networking; provide planning/ technical assistance focusing on transportation barriers to improve information sharing/ networkingInternet-based Information
MetroWest Regional Transit Authority
Expanded Medical Service
Provide a shared, one-seat ride for medical trips in MWRTA service area to locations within 25-mile radius of Framingham hubParatransit
MetroWest Regional Transit Authority
Enhanced Website and Automatic Call
Create enhanced website interface that will allow customers to access their account information and to request and cancel trips when call center is closed; also, receive confirmation email when a trip is scheduled; install automated call function that allows driver to notify the customer five minutes before pickupCapital, web site and equipment
MetroWest Regional Transit Authority
Mobility Manager
Fund a mobility manager to improve efficiency/ utilization of existing servicesMobility Management
MetroWest Regional Transit Authority
Peer-to-Peer Training Program
Training program to help MWRTA RIDE users shift onto fixed-route service; would provide one-on-one training assistance to elderly people who are losing their driver licensesTravel Training
Mission Hill Link
Capital Program
Purchase fully accessible expansion vehicle/ Charlie Card integration equipment to provide new and expanded services to individuals with disabilities traveling in area of Brigham’s Circle, Roxbury Crossing, and New England Baptist HospitalCapital, vehicle and equipment
Mystic Valley Elder Services
Mystic Valley Elder Services Connect-a-Ride Alliance
Provide new/ expanded demand-response transportation to older adults/ those with disabilities; includes central dispatch and volunteer driver programMobility Management, combination of services (including operating)
New England Paralyzed Veterans of America
Capital Program
Purchase accessible vehicles to provide transportation to medical appointments/ social events for disabled veteransCapital, purchase vehicle
New England Chapter Paralyzed Veterans of America
Transportation Service
Provide transportation to medical appointments/ social events for disabled veteransParatransit
North Shore Workforce Investment Board
Mobility Management and Employment Express
Subscription paratransit service providing access to employment corridors in Salem, Peabody, and Danvers
Mobility management includes advisory service for persons with disabilities and low-income individuals; would help them to access appropriate and affordable transportation throughout the North ShoreParatransit
SCM Transportation
Cambridge in Motion
Create mobility-management program to expand/ reinforce one-stop communication center.
Create travel-training program for individuals with disabilities; develop mobility management toolkit that can be used by other communitiesMobility Management (including travel training, one stop call center)
Note: Projects funded during multiple solicitations are only counted once.
Source: CTPS.
1 Chapter 53 of title 49, United States Code, as amended by MAP-21, Related MAP-21 provisions, p.68, October 1, 2012.